User Tools
Site Tools
Table of Contents
VCI Script Tutorial
The VCI script is implemented with Lua language.
Here, we will be using the VCI we created in Creation of VCI to write and add a script into it.
You can debug while running it in Virtual Cast.
Create script
The working folder (or workspace) for the script is
C:/Users/__USER_NAME__/AppData/LocalLow/VirtualCast/VirtualCast/EmbeddedScriptWorkspace
.
You can run the script you created in here in Virtual Cast.
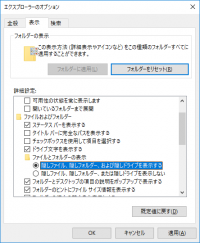
Note: If the AppData folder is hidden, in [Folder options] tick [View] > [Hidden file].
(1)Open the folder in VS Code
Open the workspace in VS Code.
In the menu, click on [File] > [Open folder] and open the path mentioned above.
It will show the directory for the workspace on the side-menu of VS Code, handy for referencing sources.
(2)Create a folder for the target VCI
When you spawn an item on Virtual Cast, a folder for the target VCI is created automatically.
For instance, if the name of the item was “VCISample,” a folder with the name “VCISample” is created.
When you imported a VCI
The folder is created with the first spawning of the VCI item.
You can edit the main.lua in this folder to rewrite the script.
The script is automatically reloaded after being saved, so you don't have to re-upload it.
(3)Create main.lua
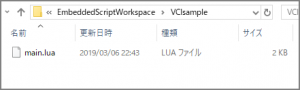 On the folder just created, create a file named “main.lua”.
We recommend you to copy [EmbeddedScriptWorkspace/template.lua] and change its name to “main.lua”.
On the folder just created, create a file named “main.lua”.
We recommend you to copy [EmbeddedScriptWorkspace/template.lua] and change its name to “main.lua”.
How to check the console
Debug setting for VCI items
From the VirtualCast settings screen, select the [VCI] tab and enable [Display debug information in the studio] to display the console in the VR space.
Features of the console
In general
- A debug console is spawned in Virtual Cast
- The console display is only visible to you and not being synced with other players
- As with other items, you can grab, move and stretch with both hands
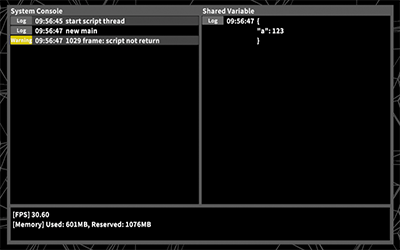
SystemConsole
- System messages for VCI scripts are displayed
- When threads stopped or became unresponsive
- When you use global sync variables, the content is shown as json1).
- Displays the current frame rate and memory usage
ItemConsole
- A console for individual items
- Generated at the time of item spawn, and will be destroyed together with the item
- You can see the following by pressing grip button while holding it
- Console
- List of SubItems
- List of Materials
- List of Animations
- List of Audios
- Statistics
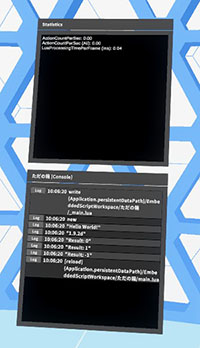
Statistics entries
| Name | Description | VC version |
|---|---|---|
| ActionCountPerSec | The number of operations (such as SetPosition) per second | 1.9.2d |
| ActionCountPerSec (ALL) | The number of _All_ operations (such as SetPosition) per second | 1.9.2d |
| LuaProcessingTimePerFrame (ms) | lua code processing time (milli second) per frame | 1.9.2d |
The lower the values shown on the statistics, the faster the processing speed of the VCI. If you feel a VCI is slow, check these values and optimize it.
Display a string on the console
- A string will be displayed on the console when you write a code shown below in a VCI script.
- main.lua
print("string")
Other debug features (for advanced creators)
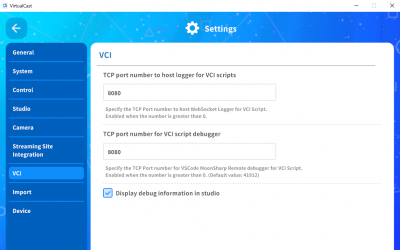
On the VCI configuration screen, specify a port number greater than 0 for [TCP port number to host logger for VCI scripts] and [TCP port number for VCI script debugger]. And access [localhost:`port number`] from a web browser while you are in the studio to view debugging information for VCI items.
Test an example script in Virtual Cast
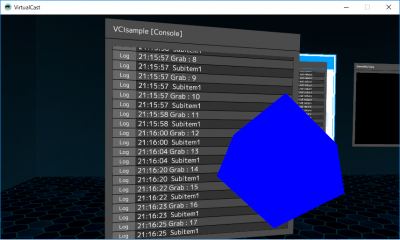
1. Copy and paste the below code into [main.lua] inside the VCI folder.
- main.lua
GrabCount = 0 function onGrab(target) GrabCount = GrabCount + 1 print("Grab: "..GrabCount) print(target) end
2. In Virtual Cast, grab the VCI object. If you see the number of times you grabbed the object on the console, it's a success.
Note: this is just a quick sample script for this tutorial.
Note: For detailed information on VCI script, see VCI Script Reference.
Embedding the VCI script
1. Open the project you used to create the VCI item, and load the Scene.
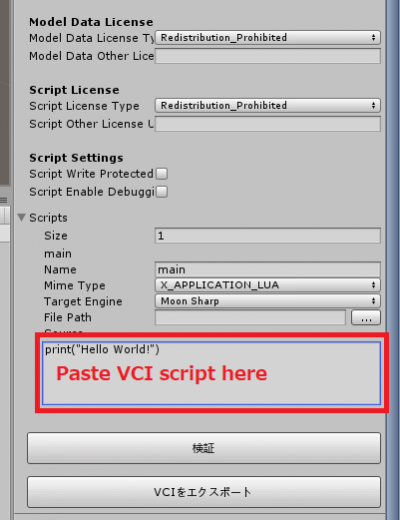
2. In [VCIObject], change [Scripts] > [Size] to 1 and press enter.
3. The inspector expands. Type the following.
[Name]: [main.lua]
[Source]: [Paste the script you created]
You may encounter an error if the code is too long (More than 1.5 thousand characters).
4. Save the Scene and once again export the VCI.
On the menu bar, select [VRM] > [UniVCI-x.xx] > [Export], and save it.
5. Overwrite the item with the new VCI you just exported. Now you have made a VCI with a script enabled.